Sachin Ramchandra Tapasvi, Anshu Shekhar, Shantanu Sudhakar Patil
Volume 1 | Issue 2 | Aug – Nov 2016 | Page 14-18
Author: Sachin Ramchandra Tapasvi [1], Anshu Shekhar [1], Shantanu Sudhakar Patil [1]
[1] The Orthopaedic Specialty Clinic, 16 Status Chambers, 1221/A Wrangler Paranjpe Road, Pune 411004.
Address of Correspondence
Dr Sachin Ramchandra Tapasvi
The Orthopaedic Speciality Clinic, 16 Status Chambers, 1221/A Wrangler Paranjpe Road, Pune 411004
Email: stapasvi@gmail.com
Abstract
Meniscus tears are common knee injuries presenting to an arthroscopy surgeon. Repairing the meniscus to salvage knee function and biomechanics is indicated where ever possible, since the problems after meniscectomy are well established now. Inside-out meniscus repair is a very useful technique to repair tears in the posterior and middle third of both menisci. Proper adherence to technique and safety incisions reduce the risks and complications to almost the level of an all-inside meniscus repair. The technique allows precise placement of sutures, causes minimal meniscus tissue trauma, has produced good healing rates, is cost-effective and is basically, an indispensable tool in the armamentarium of any knee surgeon.
Key Words: Meniscus, Meniscus repair, Inside-out, Safety incision, Complications.
Introduction
Once considered expendable, the vital role of meniscus in knee biomechanics is firmly established now. They are known for contributing to knee stability and congruity, resisting capsular and synovial impingement, load distribution and contribution towards screw home mechanism[1]. With advances in arthroscopy in terms of technique, instrumentation, optics and biomaterials, meniscus salvage has become a thrust area in this field today. The three basic techniques of meniscus repair: outside-in, inside-out and all-inside each have their indications, advantages and pitfalls. Henning et al first described the inside-out technique of meniscus repair, involving meniscal and meniscosynovial abrasion to promote healing, cannulated suture-needle delivery system for suture placement, a posteromedial or lateral skin incision for suture needle retrieval[2]. Here, we review the inside-out technique of meniscus repair.
Indications For Inside-out Repair And Technique
A meniscus tear must first be deemed suitable for repair, before deciding on the technique to be used. A non-degenerated, longitudinal tear, less than 3 centimeter and in the peripheral vascular zone is most amenable to repair[3]. An inside-out meniscus repair can be performed for the mid-third and posterior-third longitudinal tear of both the menisci[4]. With advances in all-inside meniscus repair implants and technique, this has gradually become the standard method of repair for posterior third longitudinal meniscus tears, replacing the “gold standard” method of inside-out repair[5]. Middle third tears, however, are readily amenable to repair by the inside-out technique without significant risk to neurovascular structures and possibly, without the need for a safety incision. Radial tears repaired by an all-inside or an inside-out horizontal construct have similar maximum failure loads [6]. The most recent systematic review comparing all-inside with inside-out isolated meniscus repairs did not reveal any difference in the failure rates, functional outcomes, and complications between the two methods[7]. However, the inside-out techniques has some distinct advantages. The zone specific suture needle delivery cannulae facilitate more precise and controlled suture placement, while allowing for revision and improvisation[8]. Also, the finer needles cause less iatrogenic damage to meniscus tissue, compared with the heavier all-inside implant insertion needles. This is especially vital when the meniscus tissue is tenuous, or in case of a complex tear. The finer needles also provide greater number of fixation points and captures more collagen tissue[8]. Another important advantage of inside-out repair technique is the significant savings in terms of implant cost of expensive all-inside repair devices [8].
Surgical technique
Patient position for inside-out meniscus repair can be either with a leg holder and table broken or on a flat table with thigh side support. A proximal thigh tourniquet is used for good visualization. A diagnostic arthroscopy is first performed via an anterolateral portal. A high anterolateral portal is useful if a meniscus repair is planned, to allow the needles to pass over the tibial spines without struggle. The anteromedial portal is created under vision with the aid of a spinal needle to allow easy access to medial and lateral menisci[8]. Typically, for a lateral meniscus repair, the anteromedial portal is higher to allow needles to negotiate the tibial spine[9].
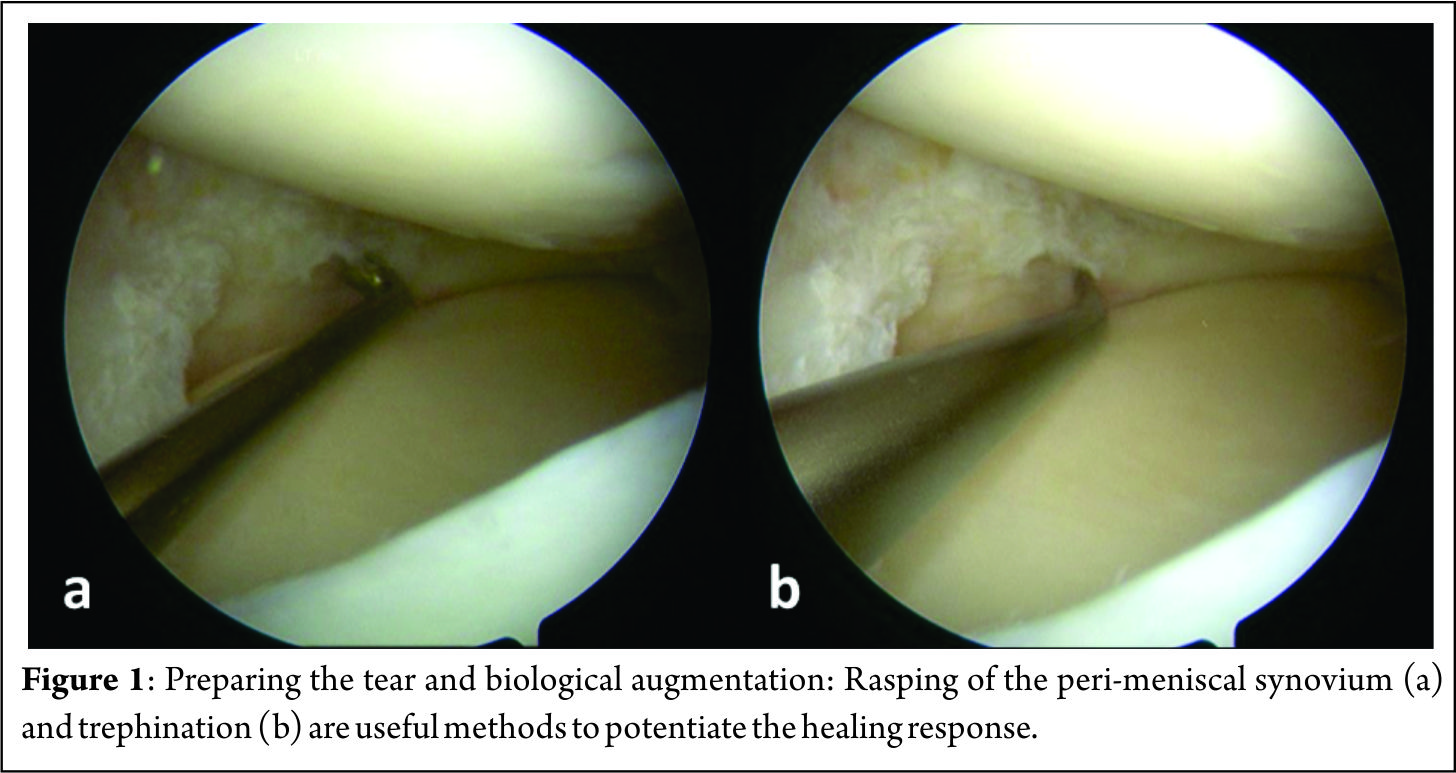
A 70 degree scope placed through the notch is helpful in viewing far posterior tears[9]. Assessment of the tear is done to decide whether to proceed with a repair or to resect the meniscus. Preparation of the meniscus tear is done next to potentiate healing. Granulation tissue must be debrided from both sides of the meniscus tear. Abrading the meniscal and peri-meniscal synovium, both superiorly and inferiorly, with a meniscus rasp (Acufex, Andover, MA) is an useful augment and aids in healing response[10]. Trephination is believed to create vascular channels and increase blood flow from a more vascular to a less vascular area[11][12]. A useful trick in bucket handle tears is to prepare the edges of the tear while the meniscus is still displaced and access to both sides is easy[8] (Figure 1). Fibrin clot prepared from the patient’s own blood is also widely used to enhance healing. It not only provides a scaffold, but also acts as an initiator and activator of the healing process[13]. When a meniscus repair is being performed in isolation, performing a limited notchplasty of the lateral femoral condyle with a shaver to create postoperative hemarthrosis and deliver marrow elements is another method of biological augmentation[9].
A. Technique for Medial meniscus inside-out repair[9]:
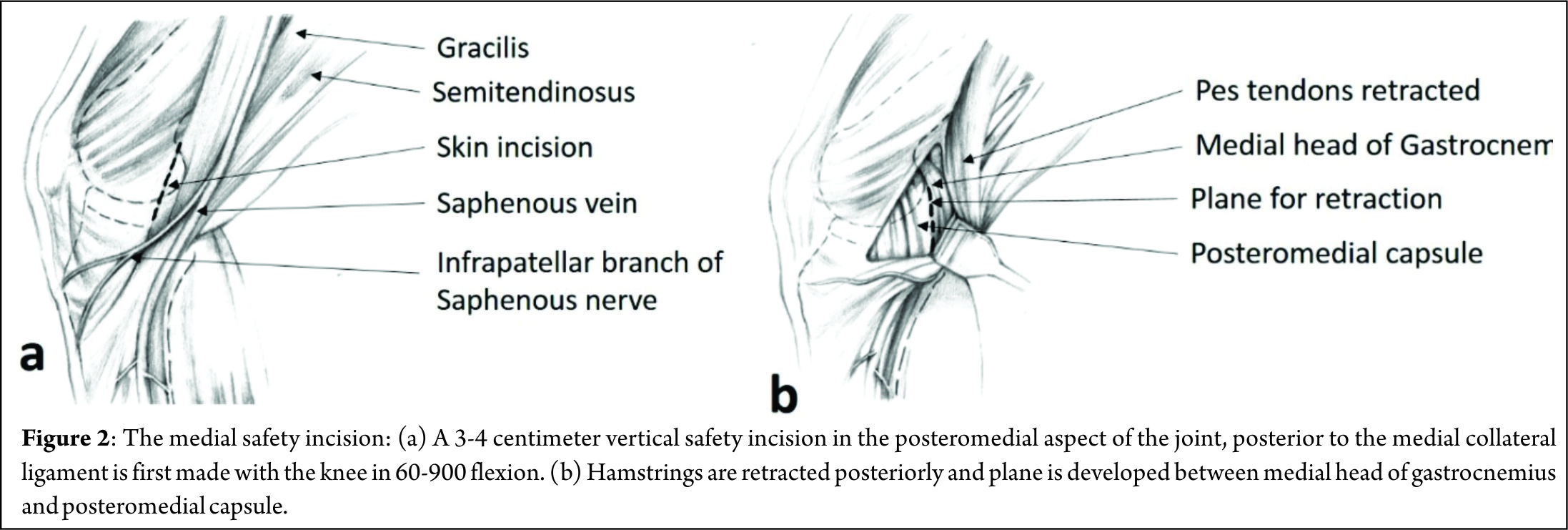
A 3-4 centimeter vertical “safety incision” (Figure 2) in the posteromedial aspect of the joint, posterior to the medial collateral ligament is first made with the knee in 60-900 flexion, to relax the hamstrings and popliteal neurovascular bundle. Transillumination aids in precise placement of this incision, with two-thirds being distal to the joint line and one-third proximal to it. The saphenous vein is carefully protected and sartorius fascia is incised and split proximally and distally with Metzenbaum scissors to preserve the Sartorius, Gracilis, Semitendinosus and the Saphenous nerve, which lies posterior to the Sartorius. Deep dissection is carried out bluntly with Metzenbaum scissors to create a plane between the medial head of gastrocnemius and capsule. This dissection is better performed from distal to proximal. Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot aids is location of the proper plane. A Henning retractor or a small bent spoon is then inserted anterior to the gastrocnemius, which protects the popliteal neurovascular bundle, retracts the pes and gastrocnemius and deflects the needle medially for retrieval. Repair can then begin, starting posteriorly and working anteriorly, with the knee in 10-200 flexion. Visualization of posterior meniscus can be improved by pie-crusting of the medial collateral ligament just below the joint line, while applying a valgus-external rotation force. Zone specific single and double lumen cannulae (Acufex, Andover, MA) inserted from the anterolateral portal are used to keep the meniscus reduced and for precise placement of the needles. For tears very close to the posterior root, it might become necessary to insert a curved cannula from the anteromedial portal, the curvature being directed away from the midline, to achieve proper trajectory for the suture needle. Non-absorbable multi-strand, long chain ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) sutures on 10 inch long needles (No. 2-0 FiberWire, Arthrex, Naples, FL) are used for the repair. The cannula is retracted 3-5 mm when the needle is pierced to increase the accuracy. This is done for the femoral side first, attempting to achieve a vertical mattress configuration, as this provides greater capture of strong circumferential fibers of the meniscus[8] (Figure 3).
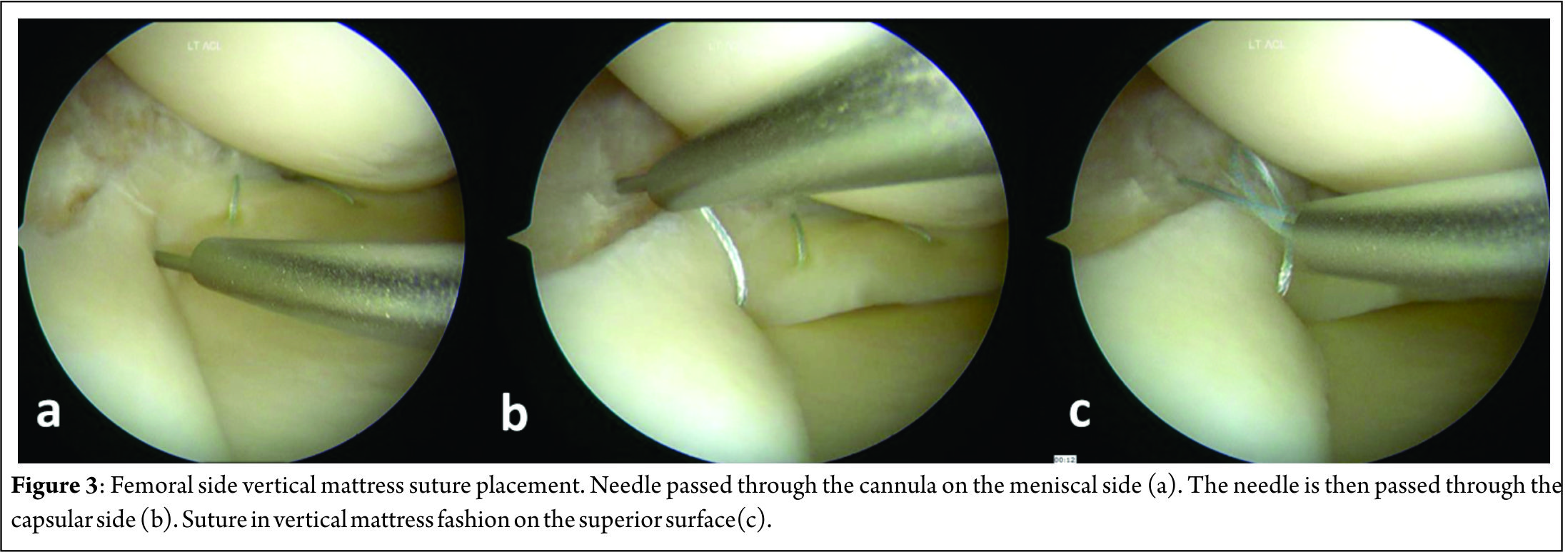
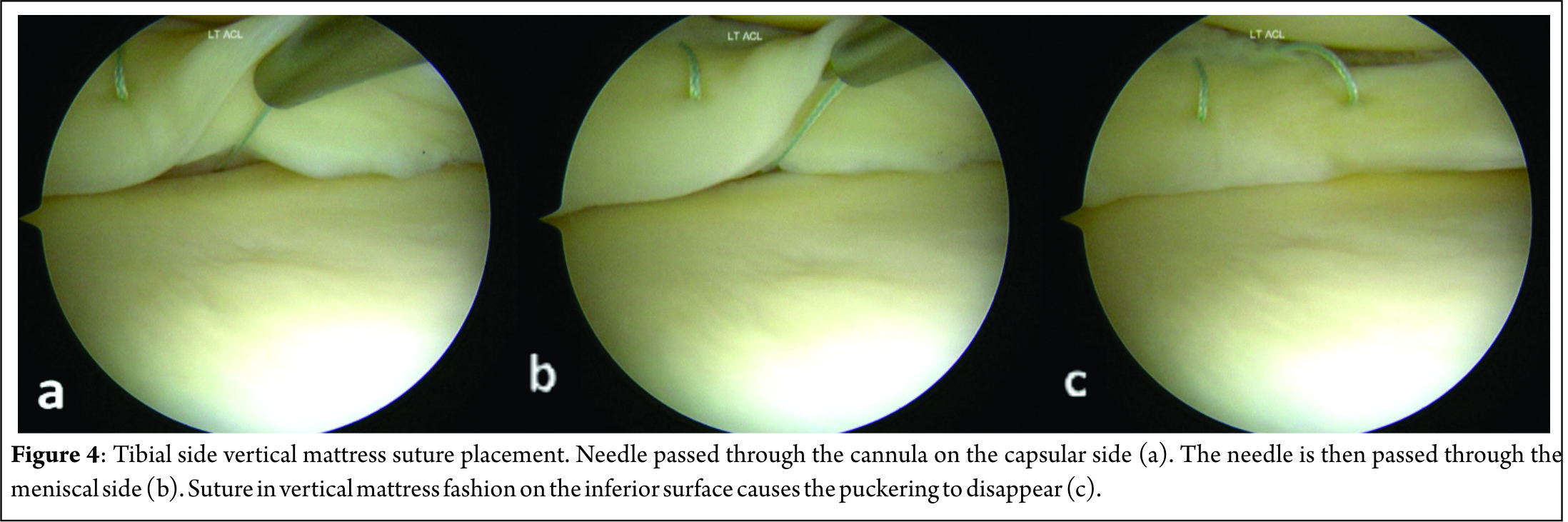
This might create a puckering of the meniscus, which subsides when tibial sided sutures are passed in a similar fashion to create a stacked repair and provide better coaptation of the tear area[14] (Figure 4). The needles are passed by one assistant, while a second assistant retrieves them using a needle driver, clips it using a hemostat and cuts the needles, taking care to avoid needle stick injury to anybody. If the needle is not visible after passing 1-1.5 centimeter, it must be withdrawn and reinserted at the same or different location with a different trajectory. Multiple sutures maybe passed at 3-5 mm intervals. The sutures may be tied sequentially as they are passed or at the end, after all have been passed out. When tying the knots, the knee must be kept in near or full extension to avoid imbricating the capsule, effectively causing a capsulorrhaphy and consequent flexion contracture. Drains may or may not be used and closure of the safety incision is done in layers.
B. Technique for Lateral meniscus inside-out repair[9]:
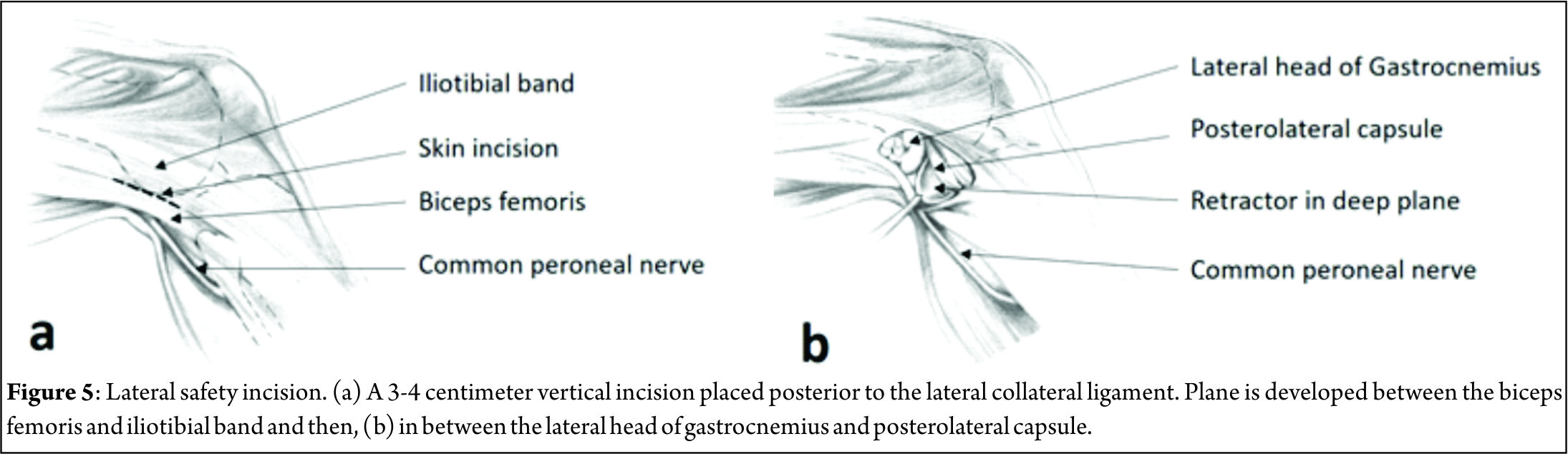
The general principles remain the same as for a medial meniscus repair, with some important differences. The lateral vertical safety incision is made in a similar fashion, posterior to the fibular collateral ligament, two-thirds distal and one-third proximal to the joint line. The interval between biceps femoris and iliotibial band is dissected bluntly with a pair of Metzenbaum scissors, the common peroneal nerve being posteromedial to the biceps tendon (Figure 5). Dissection between the lateral gastrocnemius head and posterolateral capsule is similarly begun distally and a finger is used to assess the proper plane by flexing and extending the ankle. Staying anterior to the biceps and gastrocnemius lateral head reliably protects the common peroneal nerve A Henning retractor or bent spoon is placed as for the medial side, between the capsule and gastrocnemius. The anteromedial portal is made higher to avoid the eminence of the tibial spine, under vision over a spinal needle with the knee in a figure-of-4 position. If need be, accessory high anteromedial portal can be made to improve suture needle trajectory. The cannula is never inserted from the anterolateral portal due to the potential risk to the popliteal vessels, which lie just posterior to the posterior horn of the meniscus. Though no problems have been reported, it is best to avoid the popliteus tendon and pass sutures adjacent to this structure[9]. Capsular capture is not a problem on the lateral side and hence, knot tying can be done with the knee in flexion.
Discussion
Result
The inside-out repair technique offers a success rate of 60% to 80% for isolated meniscus repairs and between 85% and 90% when performed with a concomitant ACL reconstruction[5]. Horibe et al performed second look arthroscopy for 132 meniscus repairs by inside-out technique. They report 74% excellent (completely healed) and 17% good (incomplete healing, partial thickness defect, stable on probing) result in their cohort[14]. Choi et al compared the results of suture repair of meniscus tears with concomitant ACL reconstruction, by all-inside and inside-out techniques using polydioxanone sutures. They found no difference in the healing rates on magnetic resonance imaging and no difference in Lysholm scores or Tegner activity scales between the two groups[15]. A systematic review by Grant et al was done to compare the effectiveness and complications of isolated inside-out and all-inside meniscus repairs. There was no statistical difference in clinical failure rate- 17% for all-inside and 19% for inside-out techniques. Subjective outcome, as measured by Lysholm score and Tegner activity scale was also comparable between the two groups. Inside-out repairs however, require 50% greater operative time. Nerve related symptoms were commoner (9%) in the inside-out group than in the all-inside group(2%). Upon pooling of all complication data, the Odd’s ratio was 0.55 (95% confidence interval = 0.27, 1.10). 0.55 (95% confidence interval = 0.27, 1.10)[16]. In a more recent systematic review, Fillingham et al compared current all-inside repair devices with the classical inside-out repair for isolated meniscus tears. They reported no significant differences in clinical or anatomic failure rates (clinical failure: 11% for inside-out versus 10% for all-inside, respectively, p=.58; anatomic failure: 13% for inside-out versus 16% for all-inside repairs, p=.63). Mean ± SD Lysholm score and Tegner score for inside-out repair were 88.0 ± 3.5 and 5.3 ± 1.2, while the respective scores for all-inside repair were 90.4 ± 3.7 and 6.3 ± 1.3. Complications occurred at a rate of 5.1% for inside-out repairs compared to 4.6% for all-inside repairs[7].
Complications and Problems:
The various anatomic structures in the needle trajectory can potentially be injured. By deploying safe surgical practices, they can be avoided. These are some of the commonly encountered problems:
1. Saphenous nerve injury- It can be avoided by the medial safety incision and keeping the nerve, which lies posterior to the Sartorius, retracted behind the pes tendons.
2. Common peroneal nerve injury- The nerve lies posteromedial to the biceps femoris. Injury is avoided by keeping the knee in flexion while making the lateral skin incision and carefully developing the plane between the biceps femoris and iliotibial band.
3. Popliteal vessels- are most at risk while doing a posterior lateral meniscus repair. Careful placement of retractor and always passing suture needles from the anteromedial portal with careful retrieval, avoids injury to the vessels.
4. Flexion contracture may develop- when the medial side sutures are tied with the knee in flexion, thus over tightening the posteromedial capsule.
5. Needle stick injury to the surgeon or assistants- avoided by careful, unhurried movements[8].
The inside-out technique also has an increased operative time, compared to all-inside technique by about 50%[16].
Conclusions
The inside-out method of meniscus repair is an excellent technique to repair tears in the middle and posterior-third of both menisci. With the rapid development of all-inside meniscus repair devices, this technique may not remain the “gold standard” but still has an important role, especially in repairing large and complex tears. When care is taken to protect the neurovascular structures posteriorly, and with due diligence to correct surgical technique, it is a safe, cost effective and proven method to salvage the menisci whenever possible.
References
1. Renstrom P, Johnson RJ. Anatomy and biomechanics of the menisci. Clin Sports Med. 1990 Jul;9(3):523-38.
2. Henning CE. Arthroscopic repair of meniscus tears. Orthopedics 1983; 6: 1130–1132.
3. Taylor S.A., Rodeo S.A. Augmentation techniques for isolated meniscal tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2013 Jun; 6(2): 95–101.
4. Yoon KH, Park KH. Meniscal Repair. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2014;26(2):68-76
5. Turman KA, Diduch DR. Meniscal repair: indications and techniques. J Knee Surg. 2008 Apr;21(2):154-62.
6. Branch EA, Milchteim C, Aspey BS, Liu W, Saliman JD, Anz AW. Biomechanical comparison of arthroscopic repair constructs for radial tears of the meniscus. Am J Sports Med. 2015 Sep;43(9):2270-6
7. Fillingham YA, Riboh JC, Erickson BJ, Bach BR Jr, Yanke AB. Inside-Out Versus All-Inside Repair of Isolated Meniscal Tears: An Updated Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2016 Mar 17. pii: 0363546516632504. [Epub ahead of print]
8. Nelson C.G., Bonner K.F. Inside-out meniscus repair. Arthrosc Tech. 2013 Nov; 2(4): e453–e460.
9. Bonner KF. Meniscus repair: Inside-out suture technique. In: Jackson DW, editor. Master techniques in orthopaedic surgery: Reconstructive knee surgery. Ed 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2008:71-88.
10. Ritchie JR, Miller MD, Bents RT, Smith DK. Meniscal repair inthe goat model. The use of healing adjuncts on central tears and the role of magnetic resonance arthrography in repair evaluation. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26:278–84.
11. Zhang Z, Arnold JA, Williams T, McCann B. Repairs by trephination and suturing of longitudinal injuries in the avascular area of the meniscus in goats. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23:35–41.
12. Fox JM, Rintz KG, Ferkel RD. Trephination of incomplete meniscal tears. Arthroscopy. 1993;9:451–5.
13. Ra HJ, Ha JK, Jang SH, Lee DW, Kim JG. Arthroscopic inside-out repair of complete radial tears of the meniscus with a fibrin clot. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21:2126–2130
14. Horibe S, Shino K, Maeda A, Nakamura N, Matsumoto N, Ochi T. Results of isolated meniscal repair evaluated by second-look arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 1996;12(2):150-155
15. Choi NH, Kim TH, Victoroff BN. Comparison of arthroscopic medial meniscal suture repair techniques: Inside out versus all-inside repair. Am J Sports Med 2009;37:2144-2150.
16. Grant JA, Wilde J, Miller BS, Bedi A. Comparison of inside-out and all-inside techniques for the repair of isolated meniscal tears: A systematic review. Am J Sports Med 2012;40:459-468.
| How to Cite this article:. Tapasvi SR, Anshu S, Patil SS. Inside-Out Meniscus Repair – A Review. Asian Journal of Arthroscopy Aug – Nov 2016;1(2):14-18. |